|
NVE moved up four notches in the recently-published Star Tribune 100, the largest publicly held companies with headquarters in Minnesota.
More Rankings > |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
Featured Products |
|
|
IL600-Series
Opto Replacement Isolators
The award-winning IL600
and IL600A Passive-Input Isolators provide unique passive inputs for flexibility
similar to LED-input optocouplers.
Key features are:
• MSOP packages available
• Failsafe
output
• 3.3 V or 5 V power supply
• -40°C
to 85°C temperature range
• Low EMC footprint
• 44000-year barrier life
• UL1577
recognized and IEC 61010 approved
Check out these related videos:
|
|
|
|
 How
IsoLoop Isolators Work (02:18) How
IsoLoop Isolators Work (02:18) |
|
 IL600-Series Isolators (01:30) IL600-Series Isolators (01:30) |
All
part types are in
stock and available for same-day shipment, with no minimum order:
Part
Number |
Mbps
Data
Rate |
Tx
Ch |
Rx
Ch |
Output |
Packages |
| IL610 |
100 |
1 |
0 |
CMOS |
Bare
die, MSOP-8, SOIC-8, PDIP-8 |
| IL610A |
10 |
1 |
0 |
Open-drain |
Bare
die, MSOP-8, SOIC-8, PDIP-8 |
| IL611 |
100 |
2 |
0 |
CMOS |
CMOS
MSOP-8, SOIC-8, PDIP-8 |
| IL611A |
10 |
2 |
0 |
Open-drain |
CMOS MSOP-8, SOIC-8, PDIP-8 |
| IL612 |
100 |
1 |
1 |
CMOS |
SOIC-8,
PDIP-8 |
| IL612A |
10 |
1 |
1 |
Open-drain |
SOIC-8, PDIP-8 |
| IL613 |
100 |
3 |
0 |
CMOS |
0.15"
SOIC-16, 0.3" SOIC-16 |
| IL614 |
100 |
2 |
1 |
CMOS |
0.15"
SOIC-16, 0.3" SOIC-16 |
There’s also an evaluation board that lets you try a variety of these unique isolators. The board has four IL600-Series isolators in four package types.
Download IL600 Datasheet >
Download IL600A Datasheet >
|
 |
|
|
Distributor News |
|
|
Newark
Expands NVE Distribution
 Newark/element14 is now carrying NVE Sensors in addition to isolators. Newark/ element14 is a top five North American distributor. Newark/element14 is now carrying NVE Sensors in addition to isolators. Newark/ element14 is a top five North American distributor.
The “element14” name comes from silicon, which has an atomic number of 14.
NVE products actually rely more on atomic numbers 26 through 28—ferromagnetic metals—because of their
electron-spin properties, but we’re happy to have them sold by element14.
Sensor
Distributor Network >
|
 |
|
|
Recent Exhibitions |
|
|

 NVE products were on display at PCIM Europe and Sensor+Test 2013. Both Exhibitions were in May in Nürnberg, Germany. NVE products were on display at PCIM Europe and Sensor+Test 2013. Both Exhibitions were in May in Nürnberg, Germany.
|
 |
|
|
Applications Corner |
|
|
Measuring Isolator Transient Immunity
Transient immunity is an important specification for isolators operating in noisy environments.
It’s also important in floating supply applications such as power control gate drivers.
As high-side MOSFETs turn on, there is a rapidly changing potential between the isolator output-side supply voltage and the input
reference. This changing potential can cause parasitic currents through stray capacitance proportional to
dV/dt.
IL600-Series Isolators for Gate Drivers
IL600-Series Isolators popular for gate-drive applications. IL600-Series Isolators switch based on the current through a coil analogous to optocouplers. An external resistor in the coil path typically limits the input current to the specified 5 mA. These Isolators are DC correct (meaning the output always follows the input) and failsafe (meaning the output goes to a defined state on power-down and returns to that state on power up), eliminating the need for power-on reset circuitry.
A Practical Test Setup
There are standards for fast transient immunity testing, but they do not provide a practical method.
A practical test setup to measure dV/dt in specific devices is shown below:
The setup is used to determine the maximum sinusoidal amplitude the isolator can tolerate without spurious switching.
The circuit is typical; exact values depend on the test setup.
A 20 Mhz test frequency is within the capabilities of most signal generators, and provides a reasonable dV/dt
at practical amplitudes.
A readily available 20 watt linear RF amplifier provides enough amplitude to subject the device to a high
dV/dt.
To test a device, the signal generator amplitude is gradually increased until spurious isolator outputs
occur as shown below:
The green trace is the pi network output and the purple trace is the isolator output.
Test Setup Considerations
The test setup pi network matches the 50 ohm output impedance of the RF amplifier to the device under
test. The values may need to be optimized to maximize power transfer. There are many resources for
designing pi networks, but experimenting with different inductors and capacitors may be the simplest approach.
The 330 pF and 33 nF capacitors also form a 100:1 capacitive voltage divider to bring the
voltage into the same range for the oscilloscope as the isolator output.
An oscilloscope monitors the amplitude of the driving sine wave as well as the isolator output.
The applied dV/dt can be estimated on the oscilloscope, or calculated from amplitude and frequency.
The test voltage is calculated from the oscilloscope voltage by giving effect to the 100:1
capacitive voltage divider in the pi network.
A battery drives the isolator input, with a current-limiting resistor of 1740 ohms to provide a 5 mA input
coil current. A suitable floating power can be used in place of the battery, but most laboratory supplies do
not have enough ground isolation.
While it is possible for dV/dt to also disrupt the zero coil input state,
the coil-driven state is more susceptible.
Increasing IL600 Transient Immunity
IL600-Series transient immunity increases significantly with increased input drive current by driving the
device farther into saturation. For example, increasing the input drive to 10 mA from the 5 mA minimum
can increase immunity from the specified 20 kV/µs to as much as 70 kV/µs or more.
For more information, download this Application Bulletin.
|
 |
|
|
From the Applications Desk |
|
|
Real-World Questions from the NVE Applications Desk
Q. Is input protection necessary for IL600-Series passive-input Isolators used as RS-422 / RS-485 receivers?
A. Input protection is not needed with those isolators. Conventional RS-422 / RS-485 receivers often need external input protection such as TVS to protect the semiconductor inputs.
One of the advantages of IL600-Series isolators is the inputs are simply metal coils and there are no semiconductors on the input side. This makes them extremely rugged.
Here is an illustration of an RS-485 network receiver using an IL610:
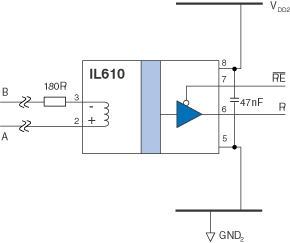 RS-485 Network Receiver with IL610 Isolator
RS-485 Network Receiver with IL610 Isolator
The 180 ohm series resistor limits the coil current below the absolute maximum input current of 25 mA with a minimum
coil resistance of 31 Ohms and a maximum differential bus voltage of 5 V. The series resistor still provides enough current to switch the isolator under worst-case conditions of 2.5 V differential bus voltage and a maximum coil resistance of 128 ohms. The coil current under these circumstances will be at least +8 mA, well above the 5 mA minimum switching threshold for the IL610.
The simple circuit minimizes chip count and board space. IL610 isolators are available in unique MSOP8s to further reduce board space.
 |
|

